Introduction
Addison’s disease also known as Primary Adrenal Insufficiency, is a rare, long-term, endocrine disorder in which the adrenal cortex (the outer layer of the cells that make up the adrenal glands) does not produce enough cortisol or aldosterone hormones.
Signs and Symptoms of Addison’s disease
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Muscle pain
- Dehydration
- Low blood pressure
- Changes in mood and behaviour
- A craving for salty food
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
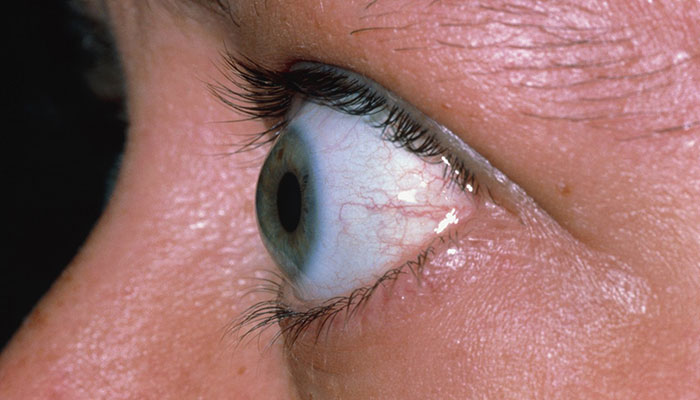
- Hyper-pigmented skin around scars
Causes of Addison’s disease
- Injury to the adrenal gland
- Tuberculosis
- Infections
- Tumours
- Excessive intake of steroids
- Autoimmune disease
- Surgical removal of adrenal glands
Understanding Addison’s disease in Ayurveda
Ayurveda states that three energy channels, Vata, Pitta, and Kapha dosha, are responsible for regulating metabolism and bodily functions. It is said that when the body’s Ojas (strength) decreases, the affected person experiences feelings of fear, worry, weakness, and mental incapacity. Ojas is believed to be the primary contributor to Addison’s disease or other adrenal disorders. The other causes of Ojas are alcohol consumption, lack of adequate sleep, trauma, and infection. According to the principles of Ayurveda, an imbalance in the Vata dosha is responsible for the symptoms of Addison’s disease.
Treatment and Management
Treatment may involve hormone replacement therapies to correct the steroid hormone levels and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Palliative care provided by SGP’s PSA for Addison’s disease focuses on symptom management through medications, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. It aims to alleviate symptoms such as extreme weakness, craving for salt, etc., improve nutritional status, and enhance overall well-being by providing emotional and psychological support.
FAQs about Addison’s disease
-
Addison’s disease is a condition in which the skin darkens in certain areas. This is due to an increase in the levels of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which binds to a pigment on the surface of the skin, resulting in a darkening of the skin.
-
Addison’s disease can be diagnosed through blood tests measuring cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels. An ACTH stimulation test can confirm this condition. Additionally, imaging studies may reveal adrenal gland abnormalities.
-
In Addison’s disease, the lack of this aldosterone causes the kidneys to constantly leak sodium (salt) from the body, causing symptoms such as dizziness, postural instability, low blood pressure, generalized weakness, cramps, and convulsions in the legs. A high sodium diet may be beneficial for individuals suffering from Addison’s disease with low aldosterone levels. Consult a healthcare provider or dietitian to determine the optimal sodium sources and recommended daily sodium intake.
-
If you have Addison’s, it’s important to make sure you eat a balanced diet that’s rich in fruits, veggies, lean protein, and calcium. You should also make sure you’re getting plenty of vitamin D and salt. Don’t eat anything high in sugar or saturated fat, and limit your intake of processed meats, grains, sugary drinks, and fried foods.
-
If left untreated, Addison’s disease may lead to severe abdominal pain, extreme fatigue, low blood pressure, kidney failure, and shock. So, it is advised to consult your healthcare provider as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed.