Lung cancer is a life-threatening condition characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in the lungs, often linked to smoking and environmental factors. Lungs are spongy organs located in the chest region that help in respiration. Lung cancer is mainly classified into two types: small-cell lung cancer and non-small-cell lung cancer. The majority of lung cancer cases, however, are non-small cell lung cancers.
Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
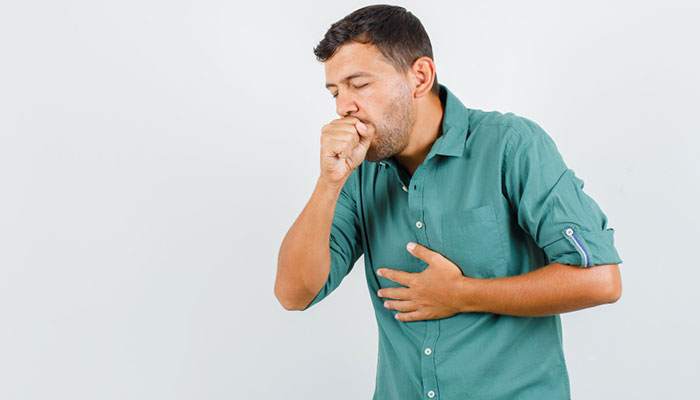
- Cough that doesn’t go away
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Hoarseness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bone pain
Causes of Lung Cancer
- Smoking tobacco
- Passive/second-hand smoking
- Consumption of arsenic-containing water
- Exposure to radon (a radioactive gas)
- Exposure to asbestos
- Exposure to cancer-causing agents
- Family history of lung cancer
- Genetics
Understanding Lung Cancer in Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, lung cancer is believed to be the result of an imbalance in the body’s doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and dhatus (body tissues). It is often associated with the accumulation of toxins in the body due to an unhealthy lifestyle, dietary choices, and exposure to environmental pollutants.
Treatment and Management
Lung cancer treatment typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. Depending on cancer’s stage and type, doctors may remove tumours through surgery, use drugs to kill cancer cells, or employ radiation to shrink tumours. Targeted therapies may be used to block specific cancer-related molecules. Treatment plans are individualized based on each patient’s condition and medical history.
Care offered by SGP’s PSA has been demonstrated to be effective in alleviating symptoms and enhancing the quality of life for patients with lung cancer. The primary focus of care delivered by the PSA is to manage symptoms, address emotional and psychological distress, and improve overall comfort.
FAQs about Lung Cancer
-
Lung cancer is diagnosed through imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans, biopsies, sputum analysis, and bronchoscopy. Early detection is crucial for determining the stage and treatment options.
-
Primary lung cancer originates in the lungs, while secondary lung cancer, also known as metastatic lung cancer, begins in another part of the body and spreads to the lungs. Treatment and prognosis differ based on their origin.
-
Common side effects of lung cancer treatment include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, hair loss, pain, cough, shortness of breath, and increased susceptibility to infections. These effects may vary with the type and stage of treatment.
-
Targeted therapy drugs specifically target certain molecules involved in cancer growth, while chemotherapy drugs affect rapidly dividing cells more broadly.
-
Lifestyle changes for lung cancer include quitting smoking, improving diet, staying active, managing stress, and getting support. These changes can enhance overall well-being and support cancer treatment and recovery.