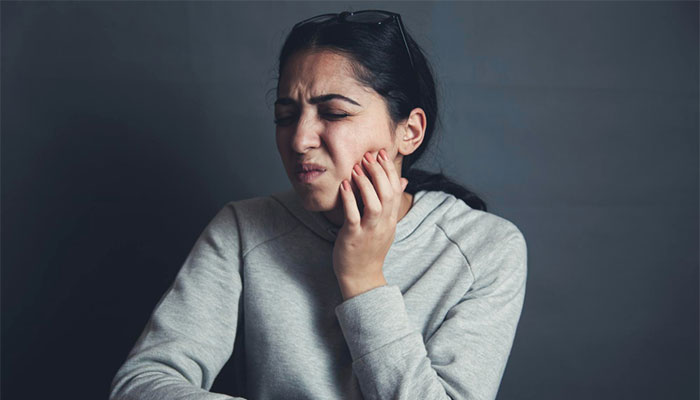
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition characterized by intense facial pain that can interfere with normal, day-to-day life. This condition can be triggered by simple actions such as chewing, speaking, smiling, brushing teeth, or shaving.
Signs and Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Numbness or a tingling sensation in the jaw/cheek area
- Short bursts of severe pain in the facial area
- Burning sensation all over one side of the face
Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia
The most common cause of trigeminal neuralgia is pressure from a blood vessel on the nerve located near the brain stem. Multiple sclerosis (MS) causes the nerve coating to deteriorate, thus trigeminal neuralgia can also be caused by MS.
Understanding Trigeminal Neuralgia in Ayurveda
In Ayurveda, Trigeminal Neuralgia is believed to be caused by an imbalance in the Vata dosha, leading to nerve compression and severe facial pain. Contributing factors may include excessive cold, wind, or stress, which aggravate Vata.
Treatment and Management
Trigeminal neuralgia is typically treated with medication, such as anticonvulsants or muscle relaxants, to manage pain. In some cases, surgical options like microvascular decompression or radiofrequency ablation may be considered.
Care offered by SGP’s PSA has been demonstrated to be effective in alleviating symptoms and enhancing the quality of life for patients with trigeminal neuralgia. The primary focus of care delivered by the PSA is to manage symptoms, address emotional and psychological distress, and improve overall comfort.
FAQs about Trigeminal Neuralgia
-
The diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia is based on the patient’s medical history, an examination of the patient’s symptoms, and a comprehensive physical examination.
-
Trigeminal neuralgia cannot always be prevented, but avoiding triggers like extreme temperatures or certain facial movements may help.
-
While some individuals experience less than one attack per day, others may experience ten or more attacks per hour. The onset of the pain is characterized by a shock sensation that increases in intensity to a painful stabbing sensation in less than twenty seconds.
-
Types of trigeminal neuralgia include:
Typical (Type 1) trigeminal neuralgia: This condition is characterized by sharp, severe, and intermittent episodes of pain. Individuals may experience pain and/or burning sensations throughout their face that may last for a few seconds or up to two minutes.
Atypical (Type 2) trigeminal neuralgia: This condition is characterized by a decrease in pain and intensity but is widespread. Individuals will likely experience constant pain, particularly stabbing and/ or burning sensations, and discomfort.
-
Women are more likely to develop trigeminal neuralgia than men and it is more common in individuals over the age of 50.