Parkinson’s disease is a progressive condition that is characterized by the deterioration of nerve cells located in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain responsible for movement. These nerve cells either die or become damaged, resulting in a decrease in the production of a chemical known as dopamine.
Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
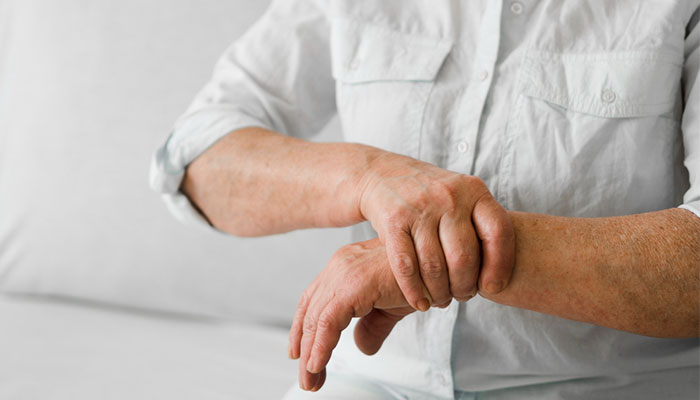
- Tremor
- Slowed movement
- Rigid muscles
- Impaired posture and balance
- Loss of automatic movements
- Changes in speech
- Changes in writing
Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
- Genes
- Environmental triggers
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease in Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, Parkinson’s disease is attributed to an imbalance in the Vata dosha, one of the three fundamental energies governing the body. This imbalance can result from factors such as poor digestion, unhealthy lifestyle, etc. These factors lead to the accumulation of Ama (toxins) and reduced nourishment of nerve tissues. This, in turn, affects the central nervous system, causing motor dysfunction and the development of Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Treatment and Management
The treatment for Parkinson’s disease primarily involves medications that increase dopamine levels in the brain. Additionally, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications can improve daily functioning. In some cases, surgical procedures like deep brain stimulation may be considered. Treatment plans are individualized, focusing on symptom management, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. Regular medical follow-ups are crucial to adjust treatment as the disease progresses.
Care offered by SGP’s PSA has been demonstrated to be effective in alleviating symptoms and enhancing the quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s disease. The primary focus of care delivered by the PSA is to manage symptoms, address emotional and psychological distress, and improve overall comfort.
FAQs about Parkinson’s Disease
-
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease involves clinical evaluation by a neurologist, considering symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. Brain imaging, such as MRI or DaTscan, may aid in confirming the diagnosis, ruling out other conditions.
-
Parkinson’s disease often causes sleep disturbances, including insomnia, restless leg syndrome, and rapid eye movement behaviour disorder. These issues can worsen motor symptoms and impact the overall quality of life for individuals with the condition.
-
There is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease. However, a range of treatments are available to assist in the management of this condition. These treatments include medication, surgery, physical, occupational and speech therapy.
-
Contrary to popular belief, Parkinson’s disease itself does not shorten life expectancy. However, in the late stages of the disease, complications such as immobilization, impaired balance, and difficulty in swallowing may be fatal.
-
Parkinson’s disease most commonly occurs after 60 years. However, about 5% to 10% of individuals experience the onset of disease before the age of 50.